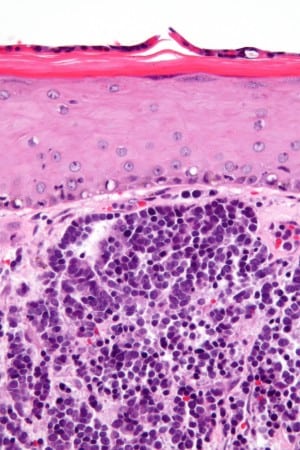
Stages of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Posted on November 4, 2015 in Skin Cancer
What are the Stages of Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
(Source)
What Are the Stages of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
KEY POINTS
- After Merkel cell carcinoma has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body.
- There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body.
- Cancer may spread from where it began to other parts of the body.
- The following stages are used for Merkel cell carcinoma:
- Stage 0 (carcinoma in situ)
- Stage IA
- Stage IB
- Stage IIA
- Stage IIB
- Stage IIC
- Stage IIIA
- Stage IIIB
- Stage IV
After Merkel cell carcinoma has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body.
The process used to find out if cancer has spread to other parts of the body is calledstaging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment.
The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process:
- CT scan (CAT scan): A procedure that makes a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body, taken from different angles. The pictures are made by a computer linked to an x-ray machine. A dye may be injected into a vein or swallowed to help theorgans or tissues show up more clearly. A CT scan of the chest and abdomen may be used to check for primary small cell lung cancer, or to find Merkel cell carcinoma that has spread. A CT scan of the head and neck may also be used to find Merkel cell carcinoma that has spread to the lymph nodes. This procedure is also called computed tomography, computerized tomography, or computerized axial tomography.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): A procedure that uses a magnet, radio waves, and a computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body. This procedure is also called nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI).
- PET scan (positron emission tomography scan): A procedure to find malignanttumor cells in the body. A small amount of radioactive glucose (sugar) is injected into a vein. The PET scanner rotates around the body and makes a picture of where glucose is being used in the body. Malignant tumor cells show up brighter in the picture because they are more active and take up more glucose than normal cells do.
- Lymph node biopsy : There are two main types of lymph node biopsy used to stage Merkel cell carcinoma.
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy : The removal of the sentinel lymph node duringsurgery. The sentinel lymph node is the first lymph node to receive lymphatic drainage from a tumor. It is the first lymph node the cancer is likely to spread to from the tumor. A radioactive substance and/or blue dye is injected near the tumor. The substance or dye flows through the lymph ducts to the lymph nodes. The first lymph node to receive the substance or dye is removed. A pathologistviews the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells. If cancer cells are not found, it may not be necessary to remove more lymph nodes.
- Lymph node dissection : A surgical procedure in which the lymph nodes are removed and a sample of tissue is checked under a microscope for signs of cancer. For a regional lymph node dissection, some of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed. For a radical lymph node dissection, most or all of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed. This procedure is also called lymphadenectomy.
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy : The removal of the sentinel lymph node duringsurgery. The sentinel lymph node is the first lymph node to receive lymphatic drainage from a tumor. It is the first lymph node the cancer is likely to spread to from the tumor. A radioactive substance and/or blue dye is injected near the tumor. The substance or dye flows through the lymph ducts to the lymph nodes. The first lymph node to receive the substance or dye is removed. A pathologistviews the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells. If cancer cells are not found, it may not be necessary to remove more lymph nodes.
- Immunohistochemistry : A test that uses antibodies to check for certain antigens in a sample of tissue. The antibody is usually linked to a radioactive substance or a dye that causes the tissue to light up under a microscope. This type of test may be used to tell the difference between different types of cancer.
There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body.
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Cancer may spread from where it began to other parts of the body.
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began (the primary tumor) and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor (metastatic tumor) in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor (metastatic tumor) in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if Merkel cell carcinoma spreads to the liver, the cancer cells in the liver are actually cancerous Merkel cells. The disease is metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma, not liver cancer.
The following stages are used for Merkel cell carcinoma:
Stage 0 (carcinoma in situ)
In stage 0, the tumor is a group of abnormal cells that remain in the place where they first formed and have not spread. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread tolymph nodes or distant parts of the body.
Stage IA
In stage IA, the tumor is 2 centimeters or smaller at its widest point and no cancer is found when the lymph nodes are checked under a microscope.
Stage IB
In stage IB, the tumor is 2 centimeters or smaller at its widest point and no swollen lymph nodes are found by a physical exam or imaging tests.
Stage IIA
In stage IIA, the tumor is larger than 2 centimeters and no cancer is found when the lymph nodes are checked under a microscope.
Stage IIB
In stage IIB, the tumor is larger than 2 centimeters and no swollen lymph nodes are found by a physical exam or imaging tests.
Stage IIC
In stage IIC, the tumor may be any size and has spread to nearby bone, muscle, connective tissue, or cartilage. It has not spread to lymph nodes or distant parts of the body.
Stage IIIA
In stage IIIA, the tumor may be any size and may have spread to nearby bone, muscle,connective tissue, or cartilage. Cancer is found in the lymph nodes when they are checked under a microscope.
Stage IIIB
In stage IIIB, the tumor may be any size and may have spread to nearby bone, muscle,connective tissue, or cartilage. Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes near the tumor and is found by a physical exam or imaging test. The lymph nodes are removed and cancer is found in the lymph nodes when they are checked under a microscope. There may also be a second tumor, which is either:
- Between the primary tumor and nearby lymph nodes; or
- Farther away from the center of the body than the primary tumor is.
Stage IV
In stage IV, the tumor may be any size and has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the liver, lung, bone, or brain.